In digital marketing, staying competitive requires the right tools to improve your online visibility. Google Search Console is a free tool from Google that provides valuable insights into your website’s performance in search results.
Through our experience managing our clients’ website maintenance, we’ve found Google Search Console to be essential. It helps us identify crawl errors, resolve indexing issues, and track search queries that drive traffic. By addressing these issues early, we’ve helped our clients boost their search visibility and site performance.
Today, we’ll share insights through this guide on how Google Search Console works and offer practical steps for fixing common issues, based on our experience managing website maintenance for a range of clients.
How Google Search Console Works
Google Search Console helps you understand how your website shows up in Google’s search results. It acts as a link between website owners and Google’s search engine.
It gives important insights into how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your site. This allows you to improve your online presence and ensure your target audience finds your content.
Setting Up Your Property
Creating a property in this tool is simple. It allows website owners to monitor and manage how Googlebot interacts with their site.
There Are Two Property Options
Domain: This option covers all subdomains and protocols (http and https) of your domain.
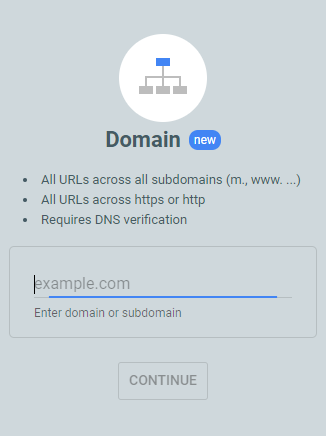
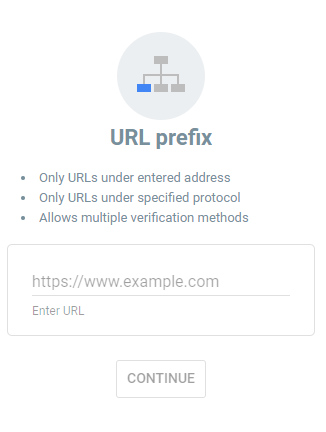
URL Prefix: This option covers a specific URL path (e.g., https://www.example.com/blog/), including all URLs that start with that prefix.
Ready To Setup Your Property? Follow This Step By Step Guide!
Sign in to Google Search Console
- Go to Google Search Console and log in with your Google account.
Add a New Property
- Click the “Add Property” button. You’ll see two options: Domain and URL prefix.
Choose the Property Type
- Domain: Covers all subdomains and multiple protocols (HTTP, HTTPS).
- URL Prefix: Limited to the specific URL you enter.
Verify Ownership
- Google needs to verify that you own the property. Verification methods include:
- HTML file upload: Download a file and upload it to your site.
- HTML tag: Add a meta tag to your site’s HTML.
- DNS record: Add a DNS record to your domain’s configuration.
- Google Analytics: Use your existing Google Analytics tracking code.
- Google Tag Manager: Use your existing Tag Manager container.
- Google needs to verify that you own the property. Verification methods include:
Check Verification Status
- After verification, you’ll get a confirmation message. If there are issues, Google will provide instructions on how to fix them.
Explore Your Dashboard
Once verified, you can access various tools and reports to monitor your site’s performance.
Note that it may take 2 to 3 days for data to become available.
Adding Users and Permissions
To manage access and permissions for your website, follow these simple steps:
- Log In: Sign in to your Google Search Console account.
- Select Property: Choose the website (property) you want to manage.
- Open Settings: Click the gear icon in the bottom left corner.
- Manage Permissions:
- Go to “Users and permissions.”
- To add a new user, click the “Add user” button.
- Enter Email: Provide the email address associated with the user’s Google account.
- Set Permission Level:
- Owner: Full control, including adding/removing users and changing settings. This can be either a verified owner or a delegated owner.
- Full User: Can view all data and perform most actions, but cannot manage users.
- Restricted User: Can view most data but cannot perform actions that change data.
- Notify User: Optionally, check the box to send an email notification to the user.
- Add User: Click “Add” to finalize the process.
Important Points:
- Only grant the necessary level of access to each user.
- Users must have a Google account linked to the provided email address.
- Users might need to verify property ownership before gaining access.
How To Integrate Your GSC Property to Google Analytics
This integration lets you view GSC data directly in your Google Analytics account. Ensure you have the Editor role in Google Analytics and Owner permission in Search Console for the accounts you want to link.
Here’s how to link GSC to Google Analytics:
- Sign in to your Google Analytics account.
- Click the “Admin” button in the lower-left corner.
- In the “Property” column, select “Property Settings.”
- Scroll to the “Search Console Settings” section.
- Confirm your website URL is verified in Search Console. If it’s not verified, add your site..
- Click “Add” to start linking Google Search Console and Google Analytics properties. Follow the on-screen instructions.
- After selecting the property to connect, click “Save.”
Note: An Analytics property can be linked to only one site, and vice versa. Creating a new link will replace any existing one.
Submitting Sitemap.xml
A sitemap.xml file serves as a guide for search engine crawlers, helping them navigate your website’s pages and content. Submitting this file to Google Search Console improves your site’s crawl efficiency.
1. Create a Sitemap
Use a sitemap generator tool or, if you use a content management system like WordPress, consider a sitemap plugin. These tools help produce an organized sitemap.xml file.
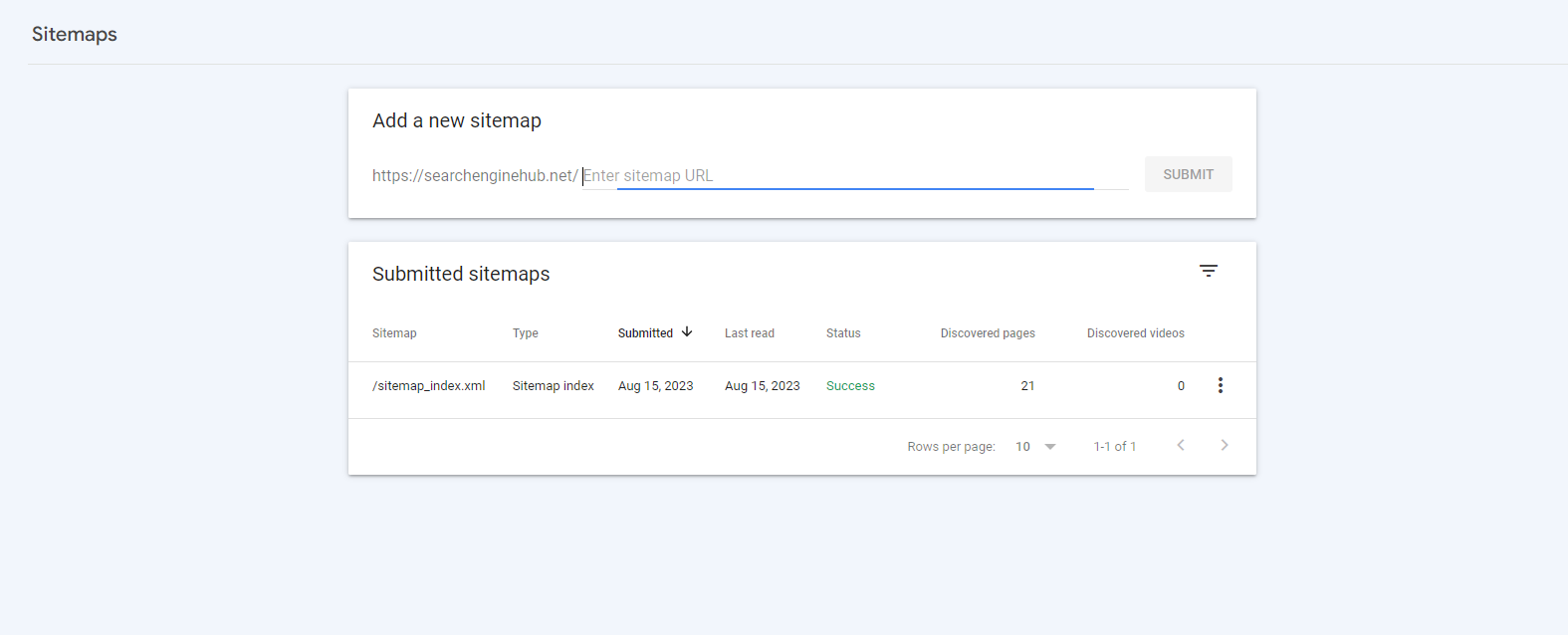
2. Submit to Google Search Console
In the dashboard, go to the “Sitemaps” section under “Indexing.” Enter the URL of your sitemap.xml file and click “Submit.” Google will start crawling and indexing the pages in your sitemap.
Common GSC Issues and Solutions
Understanding and fixing common issues in GSC is important for your website’s performance and visibility. Here are some common issues and how to solve them:
1. Indexing Issues
If you see a drop in indexed pages or suspect some content isn’t being indexed, this can affect your site’s visibility. Navigate to “Pages” under the “Indexing” tab for detailed insights into your indexed pages and any problems that need attention.
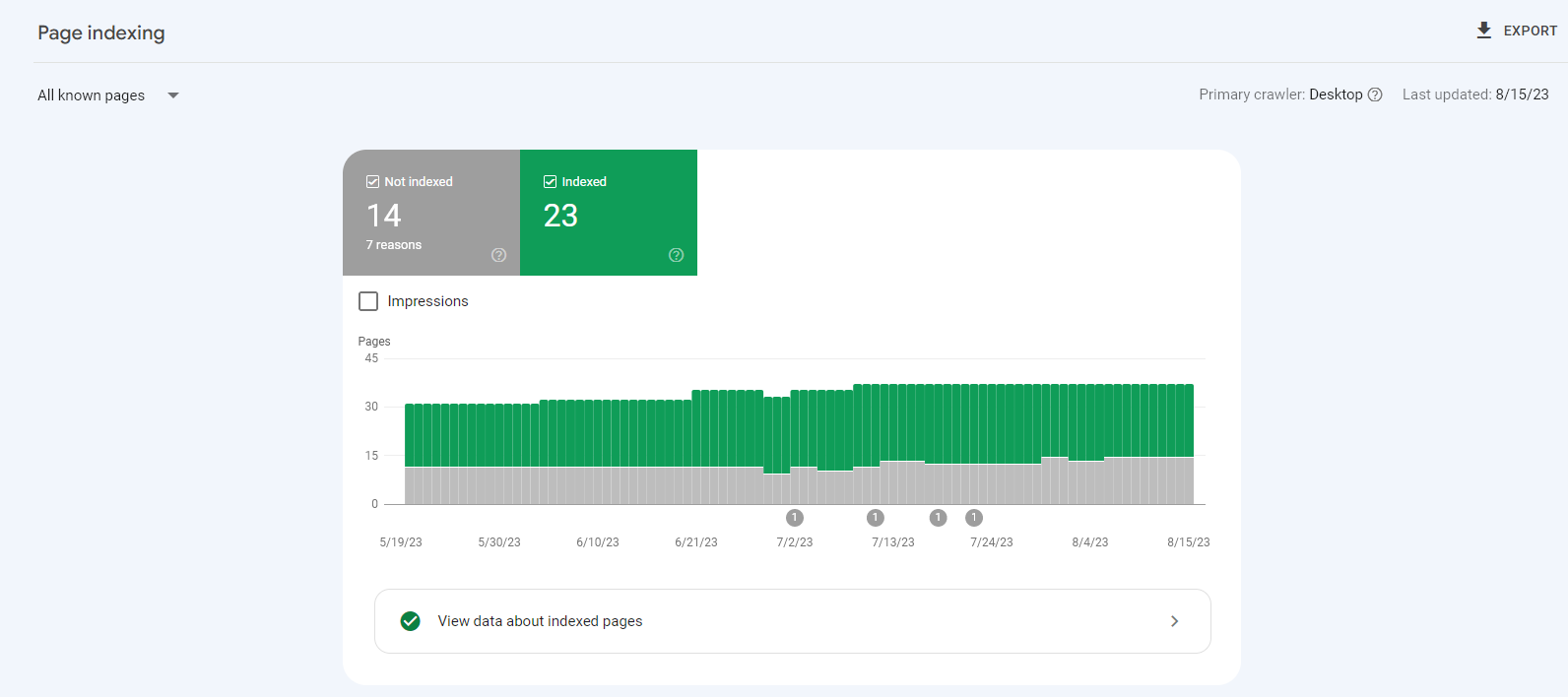
Common Indexing Issues
Crawled - Currently Not Indexed
Pages are crawled but not indexed. This may be due to low-quality content, slow loading times, or insufficient internal links. Ensure the page has valuable content, optimised images, and good internal linking.
To learn more about this issue, read our article on How to fix crawled – currently not indexed
Page with Redirect
Pages that redirect to another URL can cause indexing issues. Ensure that redirects are necessary and correctly implemented. Avoid redirect chains and loops, and check if the final destination is indexed.
To learn more about this issue, check out our article on how to fix “Page with Redirect“.
Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
When multiple pages have similar content, search engines may struggle to determine the preferred version. Specify a canonical URL to indicate which page should be indexed. This helps consolidate link equity and avoid duplicate content issues.
Alternative Page with Proper Canonical Tag
Pages that are similar but serve different purposes should have proper canonical tags. Ensure the canonical tag points to the preferred version to help search engines understand which page to index and rank.
To learn more about this issue, check out our article on Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag
Not Found (404)
Pages that return a 404 error are missing. Regularly audit your site to identify broken links. Fix or redirect broken links to relevant content, or remove the URL from your sitemap to avoid negatively impacting your site’s crawl efficiency.
To learn more about this issue, check out our article on How to fix Not found (404) error
Excluded by 'Noindex' Tag
Pages with a ‘noindex’ tag are intentionally not indexed. If you want these pages to appear in search results, remove the ‘noindex’ tag. Review your site’s robots.txt file and meta tags to ensure they’re correctly configured.
Blocked by Robots.txt
Pages blocked from crawling by the robots.txt file will not be indexed. Review and update the robots.txt file to allow crawling of important pages. Ensure you’re not accidentally blocking critical parts of your site.
Redirect Error
Incorrect redirects can lead to indexing problems. Fix any redirect loops or errors that prevent search engines from accessing the correct page. Test your redirects to ensure they lead to the intended destination without issues.
Discovered - Currently Not Indexed
Pages found by search engines but not yet indexed may suffer from crawl budget limitations or content quality issues. Improve the content, ensure it’s unique, and verify that it’s linked from other parts of your site.
To learn more about this issue, read our article on Discovered – Currently not Indexed
Soft 404
Pages that appear as not found but return a 200 status code confuse search engines. Correct the status code to 404 if the page doesn’t exist, or improve the content to make it valuable. This ensures search engines handle the page correctly.
Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical than User
When Google selects a different canonical URL than specified, it may indicate a problem with your canonical tags. Review and update your canonical tags to ensure they accurately reflect your preferred page. This helps consolidate link signals and avoid duplicate content penalties.
To find out more about this issue, check out our article on Duplicate, Google Chose Different Canonical than User.
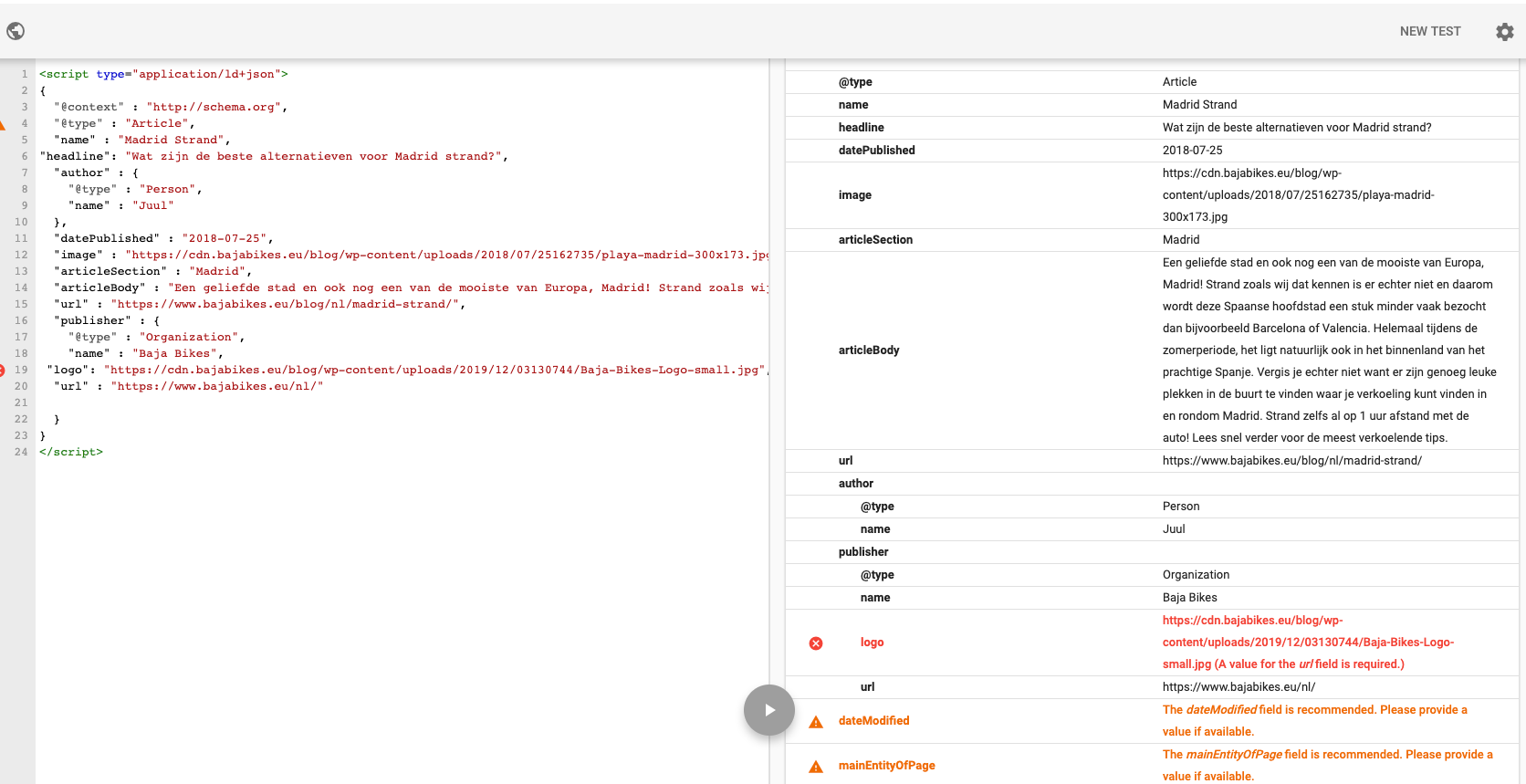
2. Structured Data Errors
Structured data, like schema markup, helps search engines understand your content and its context. Correct use of structured data can lead to rich results, such as enhanced snippets, which improve your website’s visibility and click-through rates in search results.
Common Structured Data Issues
- Invalid Markup: Incorrect structured data can cause errors. Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to check your markup and fix problems.
- Missing Properties: Include all required properties for your structured data type. Refer to Google’s official documentation for guidance.
- Duplicate Markup: Don’t use the same structured data on multiple pages unless relevant. Each page should have unique and relevant markup.
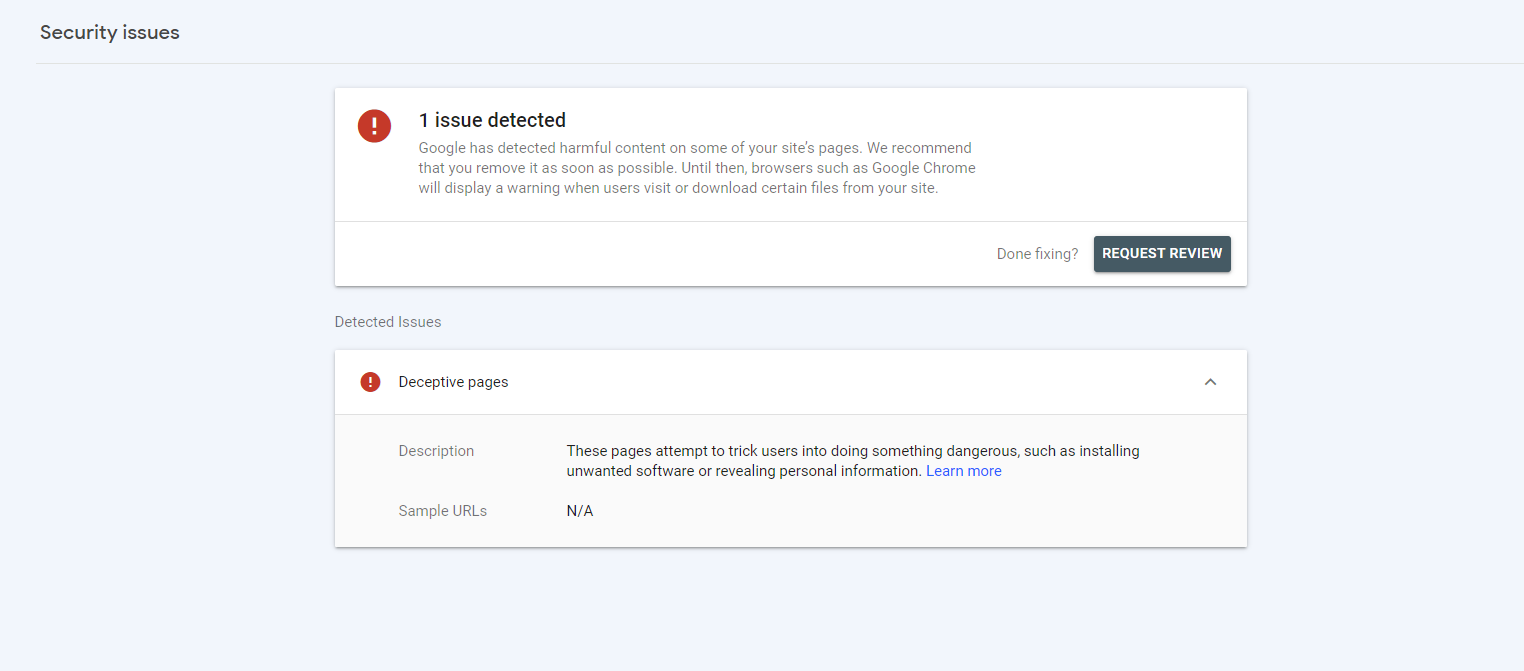
3. Security Issues
A compromised website can harm users and lower search rankings. The “Security & Manual Actions” section in Google Search Console notifies you of any security problems or manual actions taken by Google.
Common Security Issues
- Malware Infection: If your site has malware, act quickly to clean it. Scan all files and databases to remove malicious code and secure your site.
- Hacked Content: Hackers can inject harmful content or create spammy pages. Clean the affected pages, fix any security weaknesses, and enhance your site’s protection.
- Manual Actions: Google may penalise your site for guideline violations. Address the issues mentioned in the manual action notice, then submit a reconsideration request after resolving the problems.
Conclusion
Google Search Console is crucial for webmasters and marketers to improve their online presence. By understanding its features, setting up properties, integrating with Google Analytics, and solving common issues, you can manage your website effectively.
At Search Engine Hub, we help you use this tool to its fullest. Our SEO experts can identify and fix issues, enhance your site’s visibility, and support growth. Contact us to see how we can boost your online presence and achieve great results.




