A 404 error occurs when a web page cannot be found on the server, which not only frustrates users but can also harm your SEO. From our experience, addressing these errors promptly is crucial for maintaining both search rankings and a positive user experience.
Through Google Search Console, you can easily identify pages returning 404 errors. Regularly monitoring and fixing these issues helps prevent broken links and ensures that visitors can navigate your site smoothly. Whether it’s redirecting broken links or restoring missing content, taking quick action on these errors is key to keeping your site healthy.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to effectively resolve ‘not found (404)’ errors in Google Search Console, ensuring your website continues to perform well for both users and search engines.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
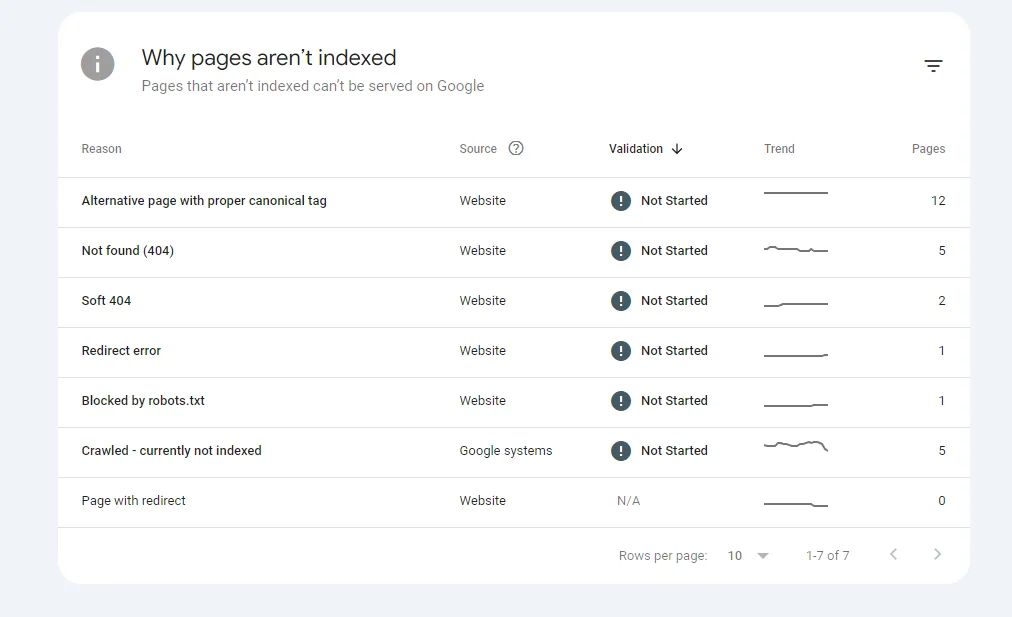
Start by locating the 404 errors in Google Search Console. Log in to your account and navigate to the Indexing section. Click on “Pages” to see the list of search console errors and other indexing issues.
Look for errors labeled “Not found (404).” This will list all URLs returning a 404 error. Additionally, Google sends an email notification if this error appears, so check your inbox for alerts.
Step 2: Analyze the Cause
Understanding why these errors occur is essential for fixing them. Common causes include deleted pages, incorrectly submitted URLs, and typographical errors.
To determine the root cause, check if the URL exists on your site and review recent changes or deletions.
Step 3: Fix Deleted Pages
If a page has been deleted, you have a couple of options:
- Redirect to a Relevant Page: Set up 301 redirects to send users and search engines to a new URL. This preserves any SEO value and ensures users find relevant content. You can set up redirects using the .htaccess file for Apache servers or plugins like Redirection or Yoast SEO for WordPress sites.
- Create a Custom 404 Page: A custom 404 page guides users back to relevant content and reduces the likelihood of them leaving your site. Include a search bar, navigation links, and a friendly message to help users find what they’re looking for.
Step 4: Correct URL Errors
For errors caused by incorrect URLs or typographical mistakes, follow these steps:
- Verify and Correct URLs: Use the URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console to check the status of the URL. If there is a mistake, correct it on your website.
- Resubmit Corrected URLs: After correcting the URL, request indexing using the URL Inspection Tool to prompt Google to re-crawl the URL and update its index.
Step 5: Prevent Future 404 Errors
Implementing seo best practices helps prevent future 404 errors. Regularly monitor Google Search Console for new 404 errors. Maintain a logical and consistent URL structure and always set up appropriate redirects when removing or moving content.
Step 6: Track and Report
Tracking and reporting ensure the errors have been resolved:
- Tools like Google Analytics can help you track 404 errors and their impact on your website’s performance. Set up custom reports to monitor these errors. You can create a custom report or use pre-made ones to identify the frequency and source of 404 errors.
- After resolving the 404 errors, use Google Search Console to validate the fixes. This lets Google know that the issues have been addressed and that the URLs should be re-crawled.
Conclusion
Fixing ‘not found (404)’ errors is important for maintaining a healthy website. By identifying the cause and resolving these errors, you can prevent broken links from harming your SEO and frustrating users. Regular monitoring and good practices can help avoid these issues in the future, ensuring a smooth user experience.
If you want ongoing support to keep your website running smoothly, check out our monthly SEO package. We can help you stay on top of issues like 404 errors while improving your site’s overall performance and SEO.




